Table of Contents
As a business proprietor, you put in many hours trying to catch the eye of your target audience. still, you will not know if all your hard work is paying off until you use an analytics tool to analyse your website.
Google Analytics in- depth reporting and web analytics tools will allow you to make the utmost of your website traffic. If you want to attract new consumers or figure out what your current audience love about your business, then this is a tool you must have.
In this blog, we’ll go over the basics of Google Analytics and show you how to start exercising it to improve your company’s operations effectively.
What is Google Analytics?
Google Analytics is a service for collecting and analysing data from websites, and can be used for SEO and marketing purposes. This feature can be accessed by any user with a Google account and is provided as part of the Google Marketing Platform.
Google Analytics monitors how well a website is doing and compiles data from visitors. It can help businesses in pinpointing the most fruitful channels through which customers enter their site, measuring the efficacy of promotional initiatives, keeping tabs on the number of customers who make a purchase or add an item to their shopping cart, and learning more about their audience’s interests and habits.
Google Analytics is extensively used by online retailers of all sizes to collect and dissect data on their customers’ online activities.
How does Google Analytics work?
Google Analytics makes use of a system of tags on each page to record information about each user’s session. Each page’s code is augmented with JavaScript tags. This tag, which is stored in the user’s browser, sends information to Google’s data- gathering services.
After configuring Google Analytics, you can generate reports detailing your site’s traffic, average session lengths, sessions by route, page views, and more.
A web beacon or web bug, like the page-tag, is placed on the page to collect information about site visitors. However, because the system relies on cookies, it will not be able to collect any information from users who have disabled them.
Users can create and save custom profiles in Google Analytics to see site-specific metrics in the future. Some of the categories that can be monitored include: content overview, keywords, referral sites, visitors review, map overlay, and traffic streams overview.
The Google Analytics dashboard can be accessed directly through the Google Analytics website, but it can also be added to other sites through a plugin or widget. Google Analytics dashboards are available from third-party providers and can be tailored to match individual requirements.
Key Terms You Need to Know
Metrics are used as a quantitative measurement standard. Users of Google Analytics can monitor up to two hundred distinct indicators of website performance. Although other measures may be more important to particular companies than others, these are among the most widely used:
Users: A user is a first-time or regular visitor to a website
Bounce Rate: The share of site visitors who didn’t navigate beyond the homepage.
Sessions: The sum of all customer interactions within a certain time frame of 30 minutes.
Average Session Duration: Average time spent on site by each unique visitor.
Percentage of new sessions: Number of unique users who have never visited the site before.
Pages per session: The typical number of pages viewed during a single session.
Goal Completions: The rate at which users perform a desired action. In other words, this is a conversion.
Page views: Total accumulated page views.
Property: The website or mobile app that you wish to monitor
Account: The home of each asset on your dashboard is called a “account.” Multiple properties can be added to a single account, or you can create separate accounts for each.
Measurement ID: A measurement ID is a special code that you insert into your site so that Google Analytics can keep tabs on it.
Event: An event is any action taken by a user on your site, such as a click, pause, or download.
Landing page: The landing page is the initial page that a website visitor encounters.
Segment: Data can be sorted by several filters, or “segments,” such as visitor type and topic.
Metrics Vs Dimensions
Metrics: These are numerical assessments of specific types of information. Examples of such metrics include total time spent on site, number of sessions, number of pages viewed each session, and average session length. Measurements can be evaluated along a number of different dimensions using metrics.
Dimensions: In order to organise and categorise information, we often employ descriptive or category attributes or labels. To compare average session length across many regions, for instance, you may utilise the “Region” dimension. As an example of a statistic, we might use “average session length” as a metric.
Google Analytics allows for the rearrangement of dimensions. Common instances of such dimensions include:
- Language
- Browser type
- City and country
- Models of devices
- User age group
Benefits of Google Analytics

Google Analytics provides a lot of benefits such as:
- The service is hassle-free, simple, and ideal for newcomers.
- A wide range of metrics and adjustable dimensions are available in Google Analytics. The platform can be used to gather a wide variety of valuable insights.
- In addition to standard analytics features like raw data tracking and reporting, Google Analytics also offers a wealth of supplementary tools for things like data visualisation, monitoring, reporting, predictive analysis, etc.
Cons of Google Analytics
- Users that disable Google Analytics cookies, specific browser extensions, ad blocking software, and privacy networks may reduce the overall accuracy of collected data.
- In order to reduce server load, reports are generated by randomly selecting 500,000 sessions. Moreover, these reports simply include error bars for the visit count. As a result, there may be substantial error margins even in relatively tiny data samples.
How to set up Google Analytics
Step 1: A Google Analytics account must be set up first. To access your existing account, simply log in.
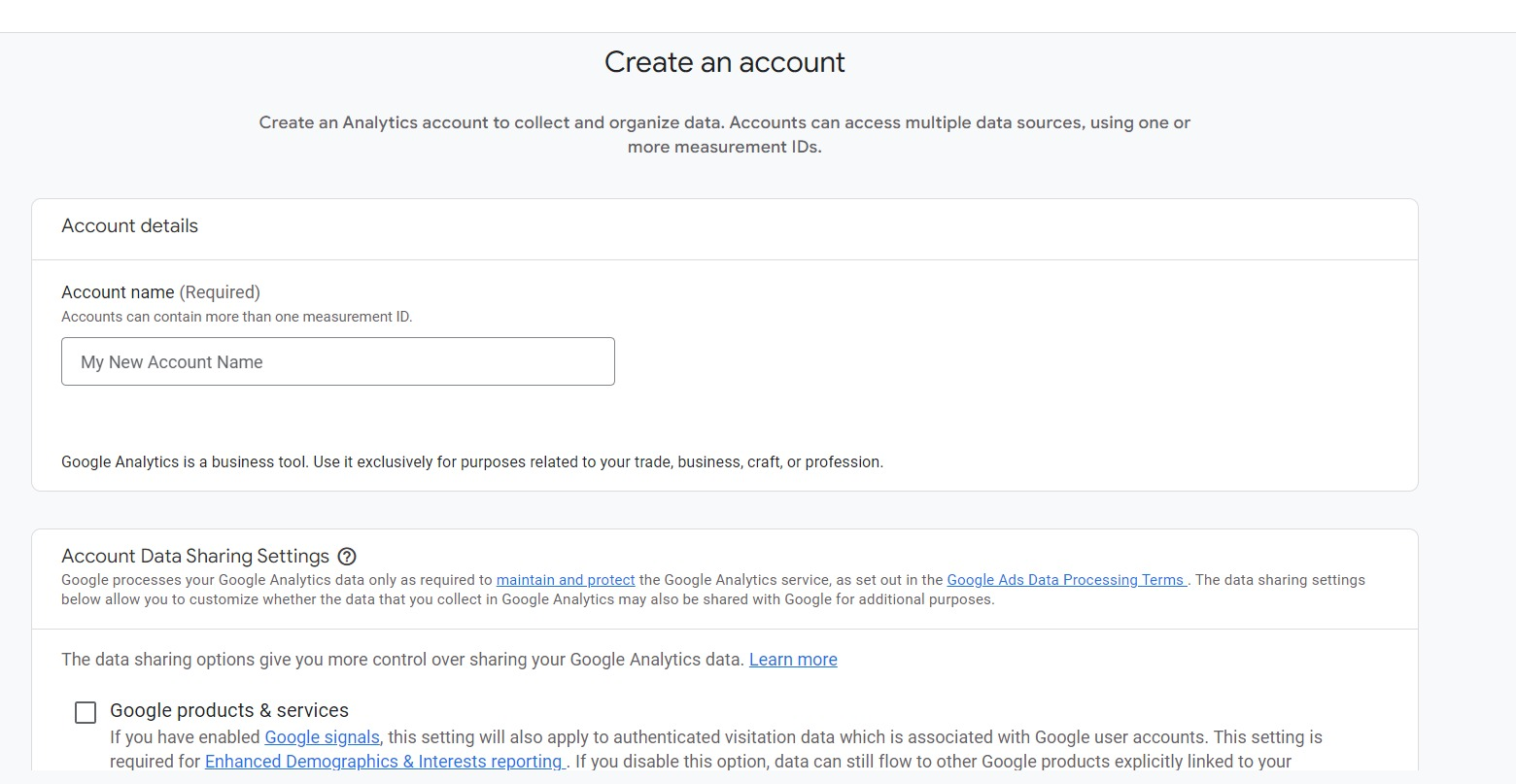
Step 2: Type in the website’s name, URL and industry sector. Create a Property, give it a name, and specify the website’s industry and reporting time zone. After that, you can proceed with Steps of Creation and Completion.
Step 3: Incorporate a Data View or Stream into your property. It must be noted that GA4 has replaced “Views” with “Data Streams” which provide the same functions.
You can create a view in Universal Analytics by going to the account and property where you want to add the view, clicking the menu item labeled Create a View, giving your view a name, choosing the view type (web or app), and answering a few more questions.
When you’re ready to add a data stream to your GA4 account, navigate to the desired account and property, then click the “Add Data Stream” option. Pick or create a new stream, then save your changes.
Step 4: Put your tracking code after the <head> tag. After a property is created, a tracking ID and a global site tag (a piece of code that must be placed on every page of the site to be measured) are made available to the owner. You can use this method to get information about your property. To properly configure the data collection, you will be prompted to select your site type (static, dynamic, web hosting, Google Tag Manager).
Step 5: Finally, make sure your code actually works. You can accomplish this by checking the Real-Time reporting area on your phone or another tab while you navigate your site. At least one user (that’s you!) should be represented in the report.
Do you need to add the GA code to every page of your site?
You just need to include the tag in all page templates. If your site only has one-page (where every page uses the same header module), then you need to add it to that module, and it will be used on all of those pages. Copy and paste the code into both header modules if you have more than one-page type. If there are three-page types, three header modules.
How to use Google Analytics?
When working with numerous accounts, properties, and views, Google Analytics makes it simple to switch between them all from the main dashboard. Find out what kind of data you can expect to see in your GA reports and how to interpret those numbers so you can use them to support strategic business choices.
On the dashboard of your Google Analytics account, you’ll discover four primary tabs:
Home
Reporting
Customisation
Admin
Home
Here you can view a snapshot of your GA account. Here you may see a list of your sites and quickly select the one you’re interested in viewing reports for. Sessions, bounce rates, goal conversion rates, etc., for each of your websites are displayed in this tab.
Reporting
Your analytics account’s Reporting page displays vital reports that shed light on your site’s performance and reveal areas ripe for optimisation. When you select Reporting, you’ll be transported to a new page specifically dedicated to the Audience Overview Report, where you can choose from the following sections:
Dashboards: Dashboards provide a snapshot of your most crucial reports and are highly adaptable because of the widgets you can add to them.
Shortcuts: Quickly access your most often consulted reports with this feature.
Intelligence Events: You can see how changes in page elements like design, content, online forms, etc. affect traffic with Google Analytics’ Content Experiments tool.
Real time Reports: Give them up-to-the-minute data on things like the number of viewers and the most popular pages or search terms.
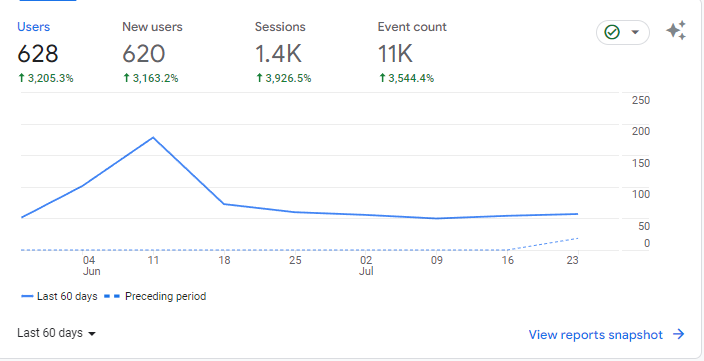
Audience Reports: You can learn more about your audience by consulting the reports they generate. Session data, including visitor locations, languages spoken, and web browsers/operating systems used, can be viewed over time intervals.
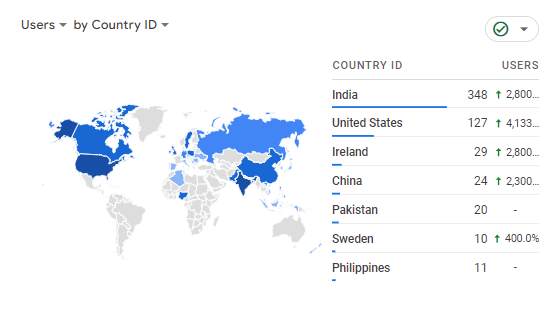
Acquisition Reports: Visitors’ Acquisition Reports reveal the paths they took to reach your site (direct, organic, referral, or social media).
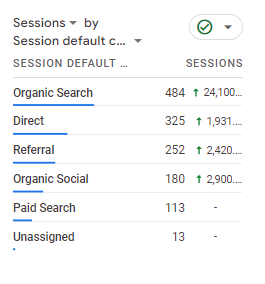
Behaviour Reports: View detailed information on how your site’s users behave with the help of Behavior Reports. You may use this information to see which of your posts are getting the most attention.
Conversions Reports: Reports on conversions give you data on how many people have converted on your site and what they did on your site before they did so.
Customisation Tab
In this section, you can tailor your own reports and keep tabs on their progress. You can make as many of these reports as you like, and they’ll all be in one place on the Customisation tab. Simply select the metric(s) you’re interested in monitoring and the dimension(s) you’d want to use to produce your report.
Metrics like bounce rate and page visits, along with dimensions like operating systems and geographic locations, are just two examples of what you could be keeping tabs on.
Admin Tab
This is where you’ll do any account-related business, including switching between accounts if you have more than one. If you have more than one website, you may select which one to view the reports for here. You can also connect your AdSense and AdWords accounts and begin tracking the success of your advertisements from this page.
User segments, attribution models, notifications, and scheduled emails can all be made in the Admin section alongside account and property management and general settings.
What is UTM?
The “Urchin Tracking Module” (or “UTM”) is an extension to a URL that provides information to Google Analytics about the source and purpose of a visitor’s visit. It’s a simple, one-of-a-kind code that can be generated quickly.
In a nutshell, UTM parameters convey the following information to Google:
From where is the activity coming?
How is it coming?
Why?
Google Analytics 4
The most recent version of Google Analytics is Google Analytics 4, or GA4, which came out in October 2020. Google Analytics 4 (GA4) is an update from earlier versions. It provides a brand-new UI and replaces the usage of third-party cookies with machine learning to improve data accuracy.
Some of the new things you can do with Google Analytics 4 are:
- Machine learning and AI tools
- Deeper integration with Google Ads
- Customеr-cеntric rеporting basеd on lifеcyclе data
- Additional data control fеaturеs for rеgulatory compliancе and data managеmеnt
- Enhancеd fеaturеs for data managеmеnt and control
Conclusion
To sum up, Googlе Analytics is a gamе-changеr for businеss ownеrs and onlinе markеtеrs. This articlе has givеn you a thorough introduction to Googlе Analytics and how you can usе it to improvе your wеbsitе’s analytics, usеr еxpеriеncе, and markеting stratеgiеs.
Googlе Analytics is a powеrful tool for monitoring a widе rangе of usеful statistics, including visits to your sitе, usеr dеmographics, and timе spеnt on your sitе. You may еnhancе thе usеr еxpеriеncе, optimisе contеnt, and incrеasе convеrsion ratеs by using statistics to makе judgmеnts about how your sitе is usеd.
Businеssеs can survivе and prospеr in today’s data-drivеn еconomy by lеarning from thеir data and using that knowlеdgе to shapе stratеgy. If you arеn’t currеntly using Googlе Analytics, you should start immеdiatеly so that you can maximisе your wеbsitе’s potеntial.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) :
Is Google Analytics free to use?
Can I track mobile app usage with Google Analytics?
Is Google Analytics compliant with data privacy regulations like GDPR?
Website owners must, however, examine their data gathering procedures to guarantee they are in accordance with applicable regulations.